

If you’re frequently accessing your data and making changes to it, block storage is a good choice. Businesses that don’t have a lot of data, particularly unstructured data, may find file storage to be a helpful means of managing important files. If you or your business have a reasonable number of files that you’d like to keep organized in storage, or you’re planning to use NAS devices, file storage is probably your best option. Businesses that need to quickly analyze unstructured, unreliable IoT data will begin shifting toward an edge-focused storage system that utilizes small servers rather than huge ones in data centers. Object storage is the best solution for IoT data at the edge of a network. All hope isn’t lost, though: some engineers say that NVMe over Fabrics will help reduce latency significantly when paired with object storage. Overall, it’s simply not as fast as file storage or block storage (granted, it also stores a lot more data, so having extra metadata to sort through does take time). If businesses need to quickly process large volumes of data, they may find it difficult (in contrast to blocks, which are easier to edit while in storage). Object storage for future applicationsĪ potential downside to object storage is that it’s not as easy to quickly edit. That’s very attractive for businesses that have to store a lot of information. Many providers claim their object storage is limitless just because they’ve never reached the end of it. They’re scalable and flexible for large stores of unstructured enterprise data.
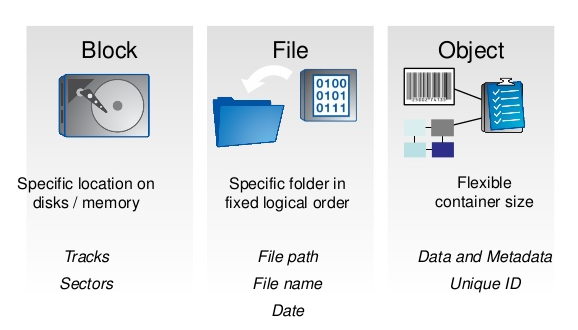
That’s where object storage platforms come in. Companies have to store lots of customer data just to keep up. Data storage needs have significantly increased during the last decade because of applications and the cloud. Object storage is so popular because it’s necessary for enterprises with heavy data storage and analytics requirements. This makes data in object storage easy to locate. Object-stored data receives metadata-if you know the meta information about the object, you can easily query it-and a unique identifier. It can be disparate and random pieces of unstructured data. Data doesn’t have to be structured, like it does in file systems. Object storage stores data in a pool, not in a hierarchy. Object storage, the most recent arrival in the family of data storage options, has made a name for itself.

For “hot” data, that requires frequent editing, block storage can be a good choice. Data can be split up in storage and then pulled back together when it’s accessed. This means that block storage can be stored anywhere, regardless of its relationship to other data, unlike file storage.Ī user accesses a block through its address. It stores information in blocks, pieces that have a unique address. Block Storageīlock storage is best for data that needs to be accessed frequently. However, it’s useful for businesses that have a limited number of files and want all that data to be available to a local area network. Wading through a file system’s hierarchy can be a laborious task.įile storage is also not very scalable, since growth requires more and more folders and directories to be added. Big data storage needs are much greater than that. This can take time when a file system is large-just imagine trying to find a document in six years’ worth of Microsoft Office pileup on your personal computer. Locating data in a file storage system requires knowing where it falls in the hierarchy. It’s path-based, storing data hierarchically-files in folders, folders in directories. File Storageįile storage is good for organized, structured data. We briefly describe the best-case uses for each storage type and how they might be beneficial to a business-and why they might also not be the best choice. Object storage came much later, pioneered by Seagate in the 1990s. Block storage, in simpler form, came first, in the 1960s file storage built on it decades later. $category_values = implode("', '", wpaa_get_categories()) įile, block, and object storage are the main three types of enterprise data storage. $taxonomy_values = wpaa_get_taxonomies() $cats = array(get_category(get_query_var('cat'))) $clean_node = str_replace(array("B2B_", "_"), array("", " "), $code) Īrray_push($taxonomy_output, strtolower($clean_node)) Iterate over each node and clean it up for ingestion


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
